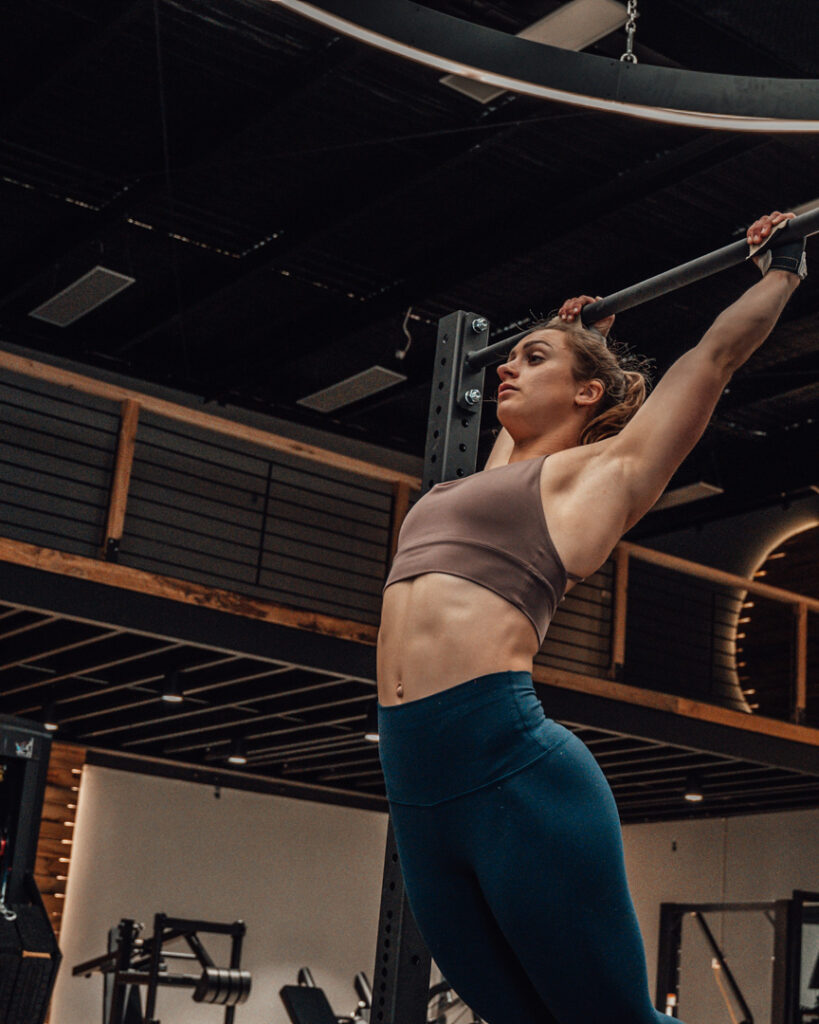Even though a kipping bar muscle up is driven primarily by momentum and good mechanics, it still requires a good strength base to do them well and safely. These basic bent-arm pushing and pulling drills will help lay the foundation for the strength you need to kip to the top of the bar.
Inverted row hold
What You’ll Need
A bar and a rack. The lower you set the bar and more you elevate your feet the harder this exercise is.
Technique
Leaving your heels on the floor, pull your elbows toward the ground until your chest touches the bar. Keep your body in a hollow position, try not to stick your chest out. Hold here for time.
Chin up
Technique
Jump up to a dead hang on the bar with an underhand grip. Squeeze your legs and abs to make a hollow body position. Pull your elbows toward the floor, trying to keep a long neck so you don’t hunch your ears around your shoulders.
Common Mistakes
Losing the hollow body position, letting the shoulders shrug up around the ears or being loose in the legs.
Ring push up
Technique
Set the rings low and form a hollow body. Do a push up as usual, noting that it may be more challenging to maintain the body line.
At the top, push hard into the rings so that your shoulder blades wrap forward around your ribs, and turn your biceps forward.
Pull up
Technique
Jump up to a dead hang on the bar with an overhand grip. If possible, bring yourself into a pseudo false grip or full false grip by aiming the base knuckle or back of hand toward the ceiling.
Squeeze your legs and abs to make a hollow body position. Pull your elbows toward the floor, trying to keep a long neck so you don’t hunch your ears around your shoulders. Complete the rep when your chin clears the bar and descend with control. If you want more challenge, aim to tap your chest below your collarbones on the bar.
Chest to bar iso holds
What is it?
A pull up with your chest touching the bar, holding yourself there to gain strength in a commonly weak position.
What You’ll Need
Very likely, a resistance band (or several) – because these are tough and most of us need to scale them to accumulate any appreciable time in this position.
Technique
Pull up until your chest is touching the bar. Hold there for time, usually 15-30 seconds.
Use as many bands as you need.
Common Mistakes
Letting the chest lose contact and still counting the rep.
Bar dips
What is it?
The easiest and usually smallest motion of the dip varieties, the bar dip primarily serves to get you used to the dip on the bar. We can build more strength with other variations but this is great for specific muscle up training.
Technique
From a support hold on the bar and in a hollow body, descend down until your chest taps the bar. Allow the elbows to travel behind you, try not to just bow to the bar. You will pike as you descend, that’s okay.
Box dips
What is it?
A dip variation that allows you to sink down between two boxes to explore a lot of range.
What You’ll Need
4 boxes or dip bars.
Technique
Dip down between the two boxes, keeping a tight body line.
Ring dips
What You’ll Need
Gymnastics rings, slung low enough to step or hop into
Technique
From a ring support, descend down between the rings without losing the hollow body position. At the top, rotate the biceps forward and make sure the rings are not touching your sides.
Common Mistakes
Try not to hug the rings too close to the sides for stability, especially at the top – this is part of embracing the challenge of the rings!
Strict negative bar muscle up
We have 3 variations of this in our kipping bar muscle up program:
- Strict negative BMU into band chair
- Strict negative BMU in low bar
- Strict negative BMU
What is it?
Practice with the strict bar muscle up, even if you’re not quite ready for a strict bar muscle up without assistance.
Technique
Keep a tight hollow body, and dip low to reduce how far you have to transition. Go as slow as you can as your elbows rotate around the bar and don’t lose your hollow body. Descend in a tight line!
Ready to workout?
Follow proven programs written by expert coaches, delivered in an easy-to-use app built by lifters, for lifters.